Many
pumps are installed with inappropriate piping arrangements, resulting in
premature pump failures, so many ways to Kill Your Pump.
If you
were installing a pump in a new system, where would you turn for guidelines on
proper pump piping arrangements?
· By following 5
simple rules, you can avoid premature pump failure and related pump piping
pitfalls :
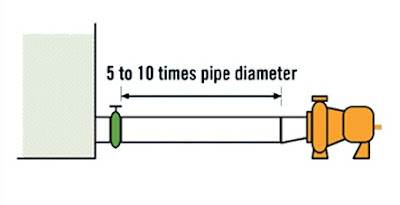
1. Keep suction pipe as short as
possible.
Include a straight run pipe length equal to 5 to 10
times the pipe diameter between the pump inlet and any obstruction in the
suction line.
Note: Obstructions include valves, elbows, "tees", and
etc.
Keeping the suction piping short ensures that inlet
pressure drop is as low as possible. The straight run pipe gives you a uniform velocity
across the pipe diameter at pump inlet.
Both are important to achieving optimal suction.
2. Pipe Diameter on suction side should be equal or one size larger
than pump inlet.
Suction piping velocities should be limited to 7 to 8
feet per second or less.
3.
Eliminate Elbows Mounted on OR Close to the inlet nozzle of the
pump
Include 5 to 10 pipe diameters of straight run pipe
between the pump inlet and elbow. This helps to eliminate "side
loading" of the pump impeller and creates uniform pump axial bearing
loading.
4.
Eliminate potential for air entertainment in the suction piping.
Maintain adequate levels in supply tanks to
eliminate vortices from forming and air entrapment.
Avoid high pockets in suction piping, which
can trap air
Keep all pipe and fitting connections tight in
suction vacuum conditions to prevent air from getting into the pump.
5.
Ensure the piping arrangement
does not cause strain on the pump casing
Pumps should never support the suction or
discharge piping. Any stress on the pump casing by the piping system greatly
reduces pump life and performance.